使用加强堆解决 topK 问题
作者:Grey
原文地址:
博客园:使用加强堆解决 topK 问题
CSDN:使用加强堆解决 topK 问题
题目描述
LintCode 550 · Top K Frequent Words II
思路
由于要统计每个字符串的次数,以及字典序,所以,我们需要把用户每次add的字符串封装成一个对象,这个对象中包括了这个字符串和这个字符串出现的次数。
假设我们封装的对象如下:
public class Word {
public String value; // 对应的字符串
public int times; // 对应的字符串出现的次数
public Word(String v, int t) {
value = v;
times = t;
}
}
topk方法的要求是: 出现次数多的排前面,如果次数一样,字典序小的排前面。
很容易想到用有序表来做。
有序表定义的比较器的规则和topk的要求一样,如果要返回topk,直接从这个有序表弹出返回给用户即可。比较器的定义如下:
public class TopKComparator implements Comparator<Word> {
@Override
public int compare(Word o1, Word o2) {
// 次数大的排前面,次数一样字典序在小的排前面
return o1.times == o2.times ? o1.value.compareTo(o2.value) : (o2.times - o1.times);
}
}
有序表配置这个比较器即可
TreeSet<Word> topK = new TreeSet<>(new TopKComparator());
所以topk()方法很简单,只需要从有序表里面把元素拿出来返回给用户即可
public List<String> topk() {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Word word : topK) {
result.add(word.value);
}
return result;
}
时间复杂度O(K)
以上步骤不复杂,接下来是add的逻辑,add的每次操作都有可能对前面我们设置的topK有序表造成影响,
所以在每次add操作的时候需要有一个机制可以告诉topK这个有序表,需要淘汰什么元素,需要新加哪个元素,让topK这个有序表时时刻刻只存topk个元素,
这样就可以确保topK()方法比较单纯,时间复杂度保持在O(K)
所以接下来的问题是:如何告诉topK这个有序表,需要淘汰什么元素,需要新加哪个元素?
我们可以通过堆来维持一个门槛,堆顶元素表示最先要淘汰的元素,所以堆中的比较策略定为:
次数从小到大,字典序从大到小,这样,堆顶元素永远是:次数相对更少或者字典序相对更大的那个元素。所以如果某个时刻要淘汰一个元素,从堆顶拿出来,然后再到topK这个有序表中查询是否有这个元素,有的话就从topK这个有序表中删除这个元素即可。
private class ThresholdComparator implements Comparator<Word> {
@Override
public int compare(Word o1, Word o2) {
// 设置堆门槛,堆顶元素最先被淘汰
return o1.times == o2.times ? o2.value.compareTo(o2.value) : (o1.times - o2.times);
}
}
如果使用Java自带的PriorityQueue做这个堆,无法实现动态调整堆的功能,因为我们需要把次数增加的字符串在堆上动态调整,自带的PriorityQueue无法实现这个功能,PriorityQueue只能支持每次新增或者删除一个节点的时候,动态调整堆,时间复杂度是O(logN),但是如果堆中的节点变化了,PriorityQueue无法自动调整成堆结构,所以我们需要实现一个增强堆,用于节点变化的时候可以动态调整堆结构,并让堆的调整保持O(logN)时间复杂度。
加强堆的核心是增加了一个哈希表,
private Map<Word, Integer> indexMap;
这个哈希表用于存放每个节点所在堆上的位置,在节点变化的时候,可以通过哈希表查出这个节点所在的位置,然后从所在位置进行heapify或者heapInsert操作,且这两个操作只会走一个,这样就动态调整好了这个堆结构,以下resign方法就是完成这个工作
public void resign(Word word) {
int i = indexMap.get(word);
heapify(i);
heapInsert(i);
}
除了这个resign方法,自定义堆中的其他方法和常规的堆没有区别,在每次进行heapify和heapInsert操作的时候,如果涉及到交换两个元素,需要将indexMap中的两个元素的位置也互换
private void swap(int i, int j) {
if (i != j) {
indexMap.put(words[i], j);
indexMap.put(words[j], i);
Word tmp = words[i];
words[i] = words[j];
words[j] = tmp;
}
}
由于自定义堆和有序表topk只存前k个数据,所以TopK结构中还需要一个哈希表来记录所有的字符串出现与否:
private Map<String, Word> map;
自此,TopK结构中的add方法需要的前置条件已经具备,整个add方法的流程如下:
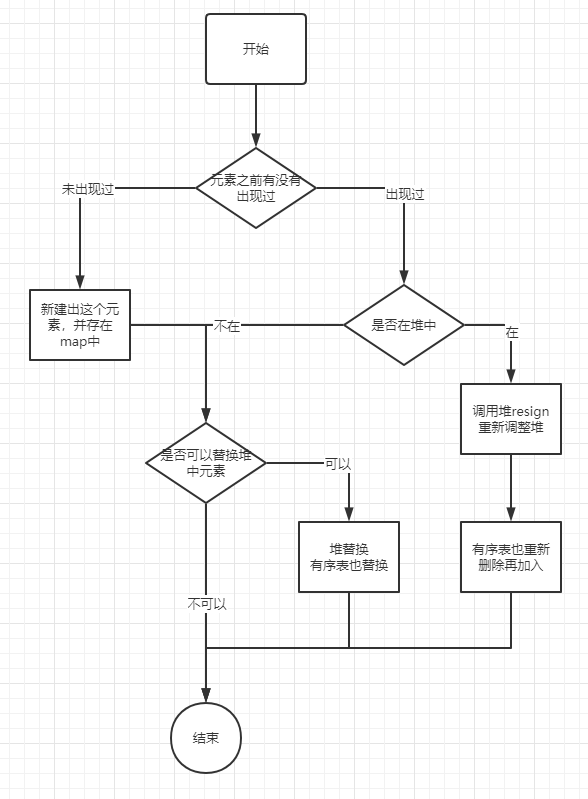
关于复杂度,add方法,时间复杂度O(log K), topk方法,时间复杂度O(K)。
完整代码
public static class TopK {
private TreeSet<Word> topK;
private Heap heap;
private Map<String, Word> map;
private int k;
public TopK(int k) {
this.k = k;
topK = new TreeSet<>((o1, o2) -> {
// 次数大的排前面,次数一样字典序在小的排前面
return o1.times == o2.times ? o1.value.compareTo(o2.value) : (o2.times - o1.times);
});
heap = new Heap(k, (o1, o2) -> {
// 设置堆门槛,堆顶元素最先被淘汰
return o1.times == o2.times ? o2.value.compareTo(o1.value) : (o1.times - o2.times);
});
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public void add(String str) {
if (k == 0) {
return;
}
Word word = map.get(str);
if (word == null) {
// 新增元素
word = new Word(str, 1);
// 是否到达门槛可以替换堆中元素
if (heap.isReachThreshold(word)) {
if (heap.isFull()) {
Word toBeRemoved = heap.poll();
topK.remove(toBeRemoved);
}
heap.add(word);
topK.add(word);
}
} else {
if (heap.contains(word)) {
topK.remove(word);
word.times++;
topK.add(word);
heap.resign(word);
} else {
word.times++;
if (heap.isReachThreshold(word)) {
if (heap.isFull()) {
Word toBeRemoved = heap.poll();
topK.remove(toBeRemoved);
}
heap.add(word);
topK.add(word);
}
}
}
map.put(str, word);
}
public List<String> topk() {
if (k == 0) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Word word : topK) {
result.add(word.value);
}
return result;
}
private class Word {
public String value;
public int times;
public Word(String v, int t) {
value = v;
times = t;
}
}
private class Heap {
private Word[] words;
private Comparator<Word> comparator;
private Map<Word, Integer> indexMap;
public Heap(int k, Comparator<Word> comparator) {
words = new Word[k];
indexMap = new HashMap<>();
this.comparator = comparator;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return indexMap.isEmpty();
}
public boolean isFull() {
return indexMap.size() == words.length;
}
public boolean isReachThreshold(Word word) {
if (isEmpty() || indexMap.size() < words.length) {
return true;
} else {
return comparator.compare(words[0], word) < 0;
}
}
public void add(Word word) {
int size = indexMap.size();
words[size] = word;
indexMap.put(word, size);
heapInsert(size);
}
private void heapify(int i) {
int size = indexMap.size();
int leftChildIndex = 2 * i + 1;
while (leftChildIndex < size) {
Word weakest = leftChildIndex + 1 < size ? (comparator.compare(words[leftChildIndex], words[leftChildIndex + 1]) < 0 ? words[leftChildIndex] : words[leftChildIndex + 1]) : words[leftChildIndex];
if (comparator.compare(words[i], weakest) < 0) {
break;
}
int weakestIndex = weakest == words[leftChildIndex] ? leftChildIndex : leftChildIndex + 1;
swap(weakestIndex, i);
i = weakestIndex;
leftChildIndex = 2 * i + 1;
}
}
public void resign(Word word) {
int i = indexMap.get(word);
heapify(i);
heapInsert(i);
}
private void heapInsert(int i) {
while (comparator.compare(words[i], words[(i - 1) / 2]) < 0) {
swap(i, (i - 1) / 2);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}
public boolean contains(Word word) {
return indexMap.containsKey(word);
}
public Word poll() {
Word result = words[0];
swap(0, indexMap.size() - 1);
indexMap.remove(result);
heapify(0);
return result;
}
private void swap(int i, int j) {
if (i != j) {
indexMap.put(words[i], j);
indexMap.put(words[j], i);
Word tmp = words[i];
words[i] = words[j];
words[j] = tmp;
}
}
}
}